Creating a unit circle graph with Processing
The challenge was to translate the Processing window coordinates into Cartesian coordinates, then create a graph of the unit circle.
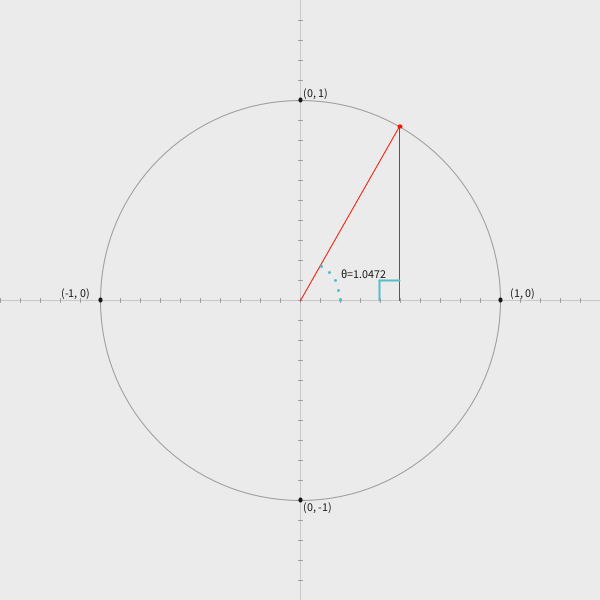
Edit: in the code below I was struggling with positioning text:
pushMatrix();
scale(1, -1);
// the y axis needs to be translated for each text y value
pushMatrix();
translate(0, -44);
String formattedRadians = String.format("%.4f", radians60);
text("θ="+formattedRadians, 41, 22);
popMatrix();
// ...
popMatrix();
That approach works, but the way I’m dealing with the y coordinate is overly complicated. Instead,
just do:
pushMatrix();
scale(1, -1);
String formattedRadians = String.format("%.4f", radians60);
text("θ="+formattedRadians, 41, -22); // use the negative of the y value that you want the text to display at
// ...
popMatrix();
Unit circle code (with overly complicated ‘y’ label placement):
size(600, 600);
textSize(12);
background(235);
noFill();
// translate to Cartesian plane for entire sketch
translate(width/2, height/2);
scale(1, -1);
stroke(200);
line(-width/2, 0, width/2, 0);
line(0, -height/2, 0, height/2);
for (int x = -width/2; x < width/2; x += 20) {
if (x % 200 == 0 && x != 0) {
stroke(100);
line(x, 4, x, -4);
} else {
stroke(155);
line(x, 2, x, -2);
}
}
for (int y = -height/2; y < height/2; y += 20) {
if (y % 200 == 0 && y != 0) {
stroke(100);
line(-4, y, 4, y);
} else {
stroke(155);
line(-2, y, 2, y);
}
}
/*
* Translation from actual scale to unit-circle scale:
* x = -1: -200
* x = 1: 200
* y = 1: 200
* y = -1: -200
*
* Distance of 0.1 is 20px
* */
// "unit" circle
ellipse(0, 0, 400, 400);
// points at each PI/2 angle
strokeWeight(4);
stroke(25);
point(200, 0);
point(0, 200);
point(-200, 0);
point(0, -200);
// an angle at 60 degrees
strokeWeight(1);
float radians60 = 60 * PI/180;
float x60 = cos(radians60);
float y60 = sin(radians60);
stroke(244, 23, 4);
line(0, 0, x60*200, y60*200);
line(x60*200, 0, x60*200, y60*200);
strokeWeight(4);
point(x60*200, y60*200);
// 90 degree angle indicator
stroke(86, 189, 199);
strokeWeight(2);
line(x60*200-20, 0, x60*200-20, 20);
line(x60*200-20, 20, x60*200, 20);
// dotted line to indicate the angle
strokeWeight(3);
stroke(86, 189, 199);
for (float theta = 0; theta < radians60; theta += 0.25) {
float x = cos(theta) * 40;
float y = sin(theta) * 40;
point(x, y);
}
// flip the scale of y to prevent text from being written upside down
fill(25);
pushMatrix();
scale(1, -1);
// the y axis needs to be translated for each text y value
pushMatrix();
translate(0, -44);
String formattedRadians = String.format("%.4f", radians60);
text("θ="+formattedRadians, 41, 22);
popMatrix();
pushMatrix();
translate(0, -6);
text("(0, 1)", 210, 3);
text("(-1, 0)", -240, 3);
popMatrix();
pushMatrix();
translate(0, -406);
text("(0, 1)", 3, 203);
popMatrix();
pushMatrix();
translate(0, 420);
text("(0, -1)", 3, -210);
popMatrix();
popMatrix();
Translating the Processing coordinate system to a Cartesian plane #
This is covered in notes / Using the Cartesian coordinate system in a Processing sketch. I confirmed that after translating the sketch’s coordinate system with:
translate(width/2, height/2);
scale(1, -1); // flip the y-axis
calls to text() need to be made with a pushMatrix()/popMatrix() block. Within that block, a call
to scale(1, -1) is made to prevent text from being rendered upside down. A call to translate(0, < -2 times the text y value >) is made to offset the effect of the call to scale(1, -1).
Formatting number strings with Java #
Numbers rendered as strings can be truncated in Processing/Java with the String.format() method.
To truncate a float’s decimal component, use the format ".4f" (with 4 or some other value
following the . character.)
Finding an x or y value when the angle and either x or y is known #
This wasn’t used in the final sketch, but for my own reference:
Say and . What’s the value of ?
Going back to SOH CAH TOA: ,
Start by converting to radians
Calculate
The above calculations were made with NumPy (64 bit precision(?)). The values calculated by Processing are similar:
size(600, 600);
textSize(12);
background(235);
noFill();
// translate to Cartesian plane for entire sketch
translate(width/2, height/2);
scale(1, -1);
stroke(200);
line(-width/2, 0, width/2, 0);
line(0, -height/2, 0, height/2);
for (int x = -width/2; x < width/2; x += 10) {
if (x % 100 == 0 && x != 0) {
stroke(100);
line(x, 4, x, -4);
} else {
stroke(155);
line(x, 2, x, -2);
}
}
for (int y = -height/2; y < height/2; y += 20) {
if (y % 100 == 0 && y != 0) {
stroke(100);
line(-4, y, 4, y);
} else {
stroke(155);
line(-2, y, 2, y);
}
}
float x = 180;
strokeWeight(4);
point(x, 0);
float angle = 28;
float angleRad = PI * angle/180;
println("28 degrees in radians: ", angleRad);
float y = tan(angleRad) * x;
println("y: ", y);
point(x, y);
line(0, 0, x, y);